Human Development Disparities and Convergence across Districts of Indonesia: A Spatial Econometric Approach
Abstract
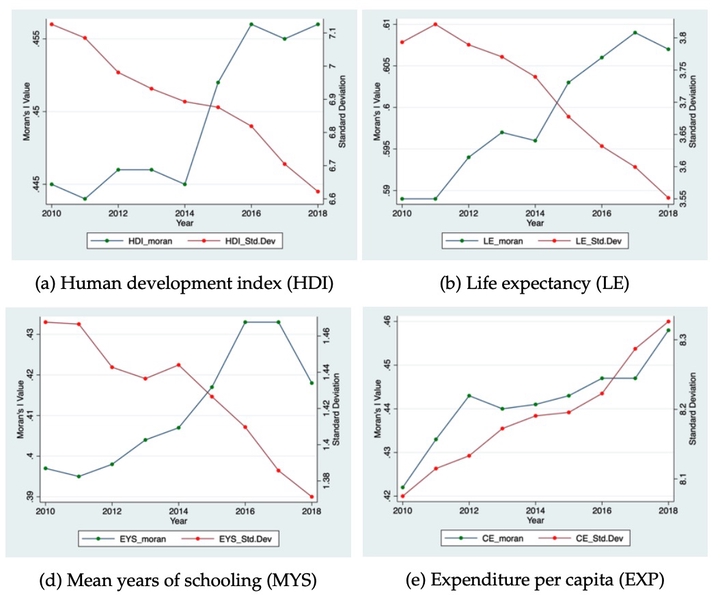
Using a novel district-level dataset of the human development index, this paper studies the evolution of regional disparities in Indonesia over the 2010-2018 period. In particular, the paper evaluates the role of spatial dependence on the speed of regional convergence. The main findings are three-fold. First, regional disparities have been decreasing in the overall index of human development as well as in most of its components. Second, there are considerable differences in the speed of convergence in the components of the human development index. Specifically, education-related components have tended to accelerate the speed of regional convergence, while life expectancy and expenditure components have tended to decelerate it. Third, there is an increasing degree of spatial dependence that is associated with the decreasing regional disparities. Moreover, results derived from spatial convergence regressions indicate that the performance of neighboring regions has a significant effect on the speed of regional convergence.