Abstract
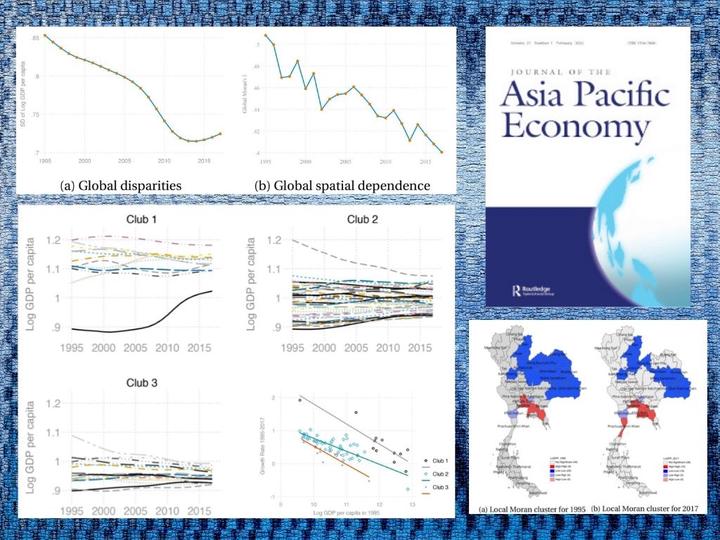
This article studies the evolution of per-capita income disparities and spatial dependence across 77 provinces of Thailand over the period 1995–2017. Results show that – on average – regional income disparities are decreasing over time and initially poor provinces are catching up with rich provinces, indicating the presence of sigma and beta convergence. However, when we study the evolution of disparities – beyond the average – we reject the hypothesis that all provinces would eventually converge to a common long-run equilibrium. The evolution of these disparities suggests the existence of three local equilibria or convergence clubs. Further analyses based on global and local indicators of spatial association reveal significant spatial dependence in the evolution of disparities and the location of the convergence clubs. This article concludes arguing that an excessive focus on global or average assessments can be incomplete, and that spatial dependence has played a significant role in the formation of local convergence clubs. Furthermore, as different clubs may need different policy treatments, there is no one-size-fits-all territorial policy for reducing regional disparities in Thailand.