Regional dynamics of luminosity-based GDP 1992-2019
When the sun goes down and the lights turn on, there’s still a lot to explore.
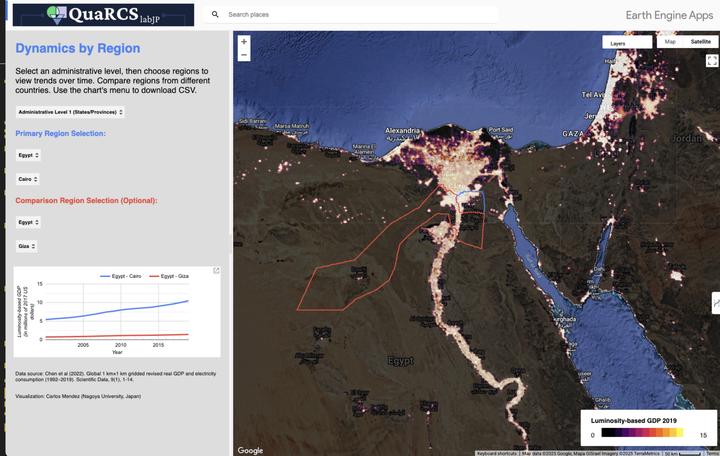
Let’s study regional development from outer space!
Let’s study regional development from outer space!
📊 Global 1 km × 1 km Gridded Revised Real GDP and Electricity Consumption (1992–2019) 🌍
📌 Introduction
- This study presents a high-resolution (1 km × 1 km) global dataset of real GDP and electricity consumption from 1992 to 2019.
- The dataset is based on nighttime light data, calibrated using a novel Particle Swarm Optimization-Back Propagation (PSO-BP) algorithm.
- The aim is to provide a more accurate and continuous measurement of economic activity worldwide.
- Citation: Jiandong Chen, Ming Gao, Shulei Cheng, Wenxuan Hou, Malin Song, Xin Liu & Yu Liu (2022). Nature Scientific Data
💡 Background & Significance
- 📈 GDP and ⚡ electricity consumption are key indicators of economic development.
- Traditional economic statistics often suffer from inconsistencies, especially in developing countries.
- 🛰️ Nighttime light data from satellites has been widely used to estimate economic output, but previous approaches had limitations in accuracy and continuity.
🗂️ Methodology
📚 Data Sources
- 🛰️ Nighttime Light Data:
- Defense Meteorological Satellite Program’s Operational Linescan System (DMSP/OLS)
- National Polar-orbiting Partnership’s Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (NPP/VIIRS)
- 📊 GDP Data: Official GDP statistics from 175 countries, revised using nighttime light data.
- ⚡ Electricity Consumption Data: Collected for 134 countries.
⚙️ Data Processing & Calibration
- 🖥️ Image Unification:
- Applied PSO-BP algorithm to standardize DMSP/OLS and NPP/VIIRS data.
- Adjusted for sensor inconsistencies and temporal discontinuities.
- 📍 Grid-Level Estimation:
- GDP and electricity consumption distributed using a top-down approach.
- Revised real GDP growth based on a weighted combination of official statistics and nightlight-derived estimates.
- 🛠️ Correction Mechanisms:
- Eliminated biases in nighttime light intensity.
- Accounted for regional heterogeneity in economic activities.
- Applied inter-annual continuous series correction to ensure temporal consistency in nighttime light data.
🔍 PSO-BP Algorithm for Data Calibration
🔄 Training Process:
- Used artificial neural networks to train a model mapping relationships between GDP, electricity consumption, and nighttime light intensity.
- Divided the data into training (60%) and testing (40%) samples.
- Applied Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) to optimize the Back Propagation (BP) neural network.
- Iterated 50 times with 20 population size to refine model accuracy.
📉 Data Matching Across Sensors:
- Addressed discrepancies between DMSP/OLS (1992–2013) and NPP/VIIRS (2012–2019) by:
- Applying pixel-level calibration.
- Ensuring consistency in spatial patterns by matching high/low DN values.
- Normalizing DN values and applying machine learning for seamless integration.
- Addressed discrepancies between DMSP/OLS (1992–2013) and NPP/VIIRS (2012–2019) by:
📊 Estimation of GDP and Electricity Consumption:
- Derived GDP growth rate as a function of official GDP and nighttime light data.
- Applied weights (ρ = 0.94 for developed countries, ρ = 0.66 for developing countries) to adjust official GDP growth.
- Estimated electricity consumption growth using a combined function of GDP and light intensity growth.
🔬 Technical Validation
✔️ Validity Testing for Nighttime Light Data
- 🏙️ Urban Built-up Areas Validation: Compared estimated urban built-up areas with official MCD12Q1 land cover data, showing high accuracy.
- 🌎 Cross-sectional Analysis: Strong correlation (R² ~ 0.87) between sum of DN values and national GDP/electricity consumption.
- Validated temporal consistency of corrected light data across years.
🤖 Validation of PSO-BP Algorithm
- Trained the PSO-BP model using national GDP, electricity consumption, and nighttime light data.
- Achieved an R² > 0.99 in training and testing datasets, confirming model robustness.
- Outperformed previous models with improved spatiotemporal consistency.
- Compared simulated GDP/electricity consumption with external datasets, showing strong alignment.
📊 Key Findings
- 📈 Improved GDP Estimation:
- The revised GDP dataset offers better accuracy than official statistics, particularly for developing nations.
- Provides a more granular view of economic activities at a local level.
- ⚡ Electricity Consumption Trends:
- The dataset captures industrial and residential electricity use trends.
- Highlights regional disparities in energy access and usage.
- 📊 Validation Results:
- High correlation (R² > 0.96) between estimated and actual GDP/electricity consumption values.
- Comparison with external data sources shows significant improvement over previous models.
🌎 Applications & Implications
- 📊 Economic Research:
- Enables detailed studies on economic growth patterns.
- Useful for policy-making in regional development.
- ⚡ Energy Policy & Planning:
- Helps in assessing energy demand and infrastructure needs.
- Supports sustainable energy policy formulation.
- 🌪️ Disaster Impact Analysis:
- Can be used to evaluate economic impacts of natural disasters.
- Provides data for rapid response planning.
✅ Conclusion & Takeaways
- This dataset provides a valuable tool for researchers, economists, and policymakers.
- The methodology ensures high accuracy and continuity over nearly three decades, offering new insights into global economic trends.
- The dataset enables micro-level analysis, particularly for regions with poor economic statistics.
- The integration of satellite-derived economic indicators with official statistics enhances data reliability.
- Future improvements may include:
- Integration with additional socioeconomic indicators to enhance model robustness.
- Refinements in machine learning techniques to further reduce errors in estimation.
- Expanding coverage to additional datasets that improve understanding of regional economic disparities.
📖 References
- Full dataset and methodology details are available at Nature Scientific Data.
- GEE dataset Access: Awesomme GEE community catalog
- Exploratory Tool: GEE web app by Carlos Mendez
See app in full screen HERE